Wait statement
source this playlist on VHDL design.
Wait statement
- More appropriate, verstail, and more useful way to manage flow in a process
- It can be used in a process and it causes a process to wait
ways to used wait statement
- 4 ways to use wait statement, some uses are unsynthesizable
unconditional wait
- causes a process to freeze until the end of simulation
- not synthesizable
- Special case of wait for - wait forever
process
begin
reset <= '1';
wait for 200ns;
reset <= '0';
wait;
end process;
wait for certain amount of time
- not synthesizable
process begin clk <= '1' wait for 200ns; clk <= '0'; wait for 200ns; end process; -- a clock signal with period = 400ns
wait until condition;
- A condition is written to wait on it becoming true
process
begin
wait until clk'event and clk='1';
Q <= D;
end process;
wait on list of signals
- A list of signals is written to pause the process till an event happens on them
process
begin
if sel="00" then
Q <= A;
elsif sel="01" then
Q <= B;
elsif sel="10" then
Q <= C;
else
Q <= D;
end if;
wait on sel, A, B, C, D; -- sensitivity list
end process;
Wait statement and senstivity list
When we use a process we can either use a process with a sensitvity list, or a process that contains wait statements, we cannot use a both at the same time mutually exclusive
Rules to understand about how the process is executed
- At startup, the process executes, so the process always execute at least once when the process starts up
- The process always loops when it ends, it never fails to loop back when it reaches the end process statement
- The process will freeze at a wait statement
effect of wait statement on events and transactions
- A signal assignment in a process is a transaction not an event
- Transactions become events only when we reach a wait statement
- If there is wait statements in the process and you reach the end of the process without a wait statement, all transactions that have not turned into event are trashed
- A process with a sensivity list is a process with wait on statement at the end of the process
- So the cardinal rule of when transaction turn into an event, is A transaction turns into an event only when it meets wait statement
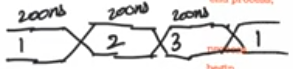
process
begin
Din <= conv_std_logic_vector(1,4);
wait for 200ns;
Din <= conv_std_logic_vector(2,4);
wait for 200ns;
Din <= conv_std_logic_vector(3,4);
wait for 200ns;
Din <= conv_std_logic_vector(4,4);
end process;
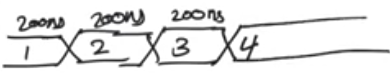
process
begin
Din <= conv_std_logic_vector(1,4);
wait for 200ns;
Din <= conv_std_logic_vector(2,4);
wait for 200ns;
Din <= conv_std_logic_vector(3,4);
wait for 200ns;
Din <= conv_std_logic_vector(4,4);
wait;
end process;
verdict on wait statement
- wait for and unconditional wait statements are generally unsynthesizable and should only be used in the test bench
- wait until statement can be used to create loops or flip flops but there is syntax that is clearer that can do both things
- wait on statement can be used to create processes that behave as if they have a sensitivity list