special port mapping
source this playlist on VHDL design.
Port mapping
- All ports have to be connected, even inputs that are don’t care, even outputs that are not used have to be connecte, maybe to an open circuit.
- input_a => (others => ‘0’), connect input a to a (bus, register, locations) carrying all zeros, it’s better to use this cause it makes code scalable
- others syntax is useful when you want to concatenate a string of ones or zeros to complete a certain port or a certain register
- Input_b => external_input(8 downto 0) & (others => ‘1’),
- output_a => open, connects the output to an open circuit
- Input_c => conv_std_logic_vector(9,16), this function converts the integer number 9 to a standard logic vector of width 16
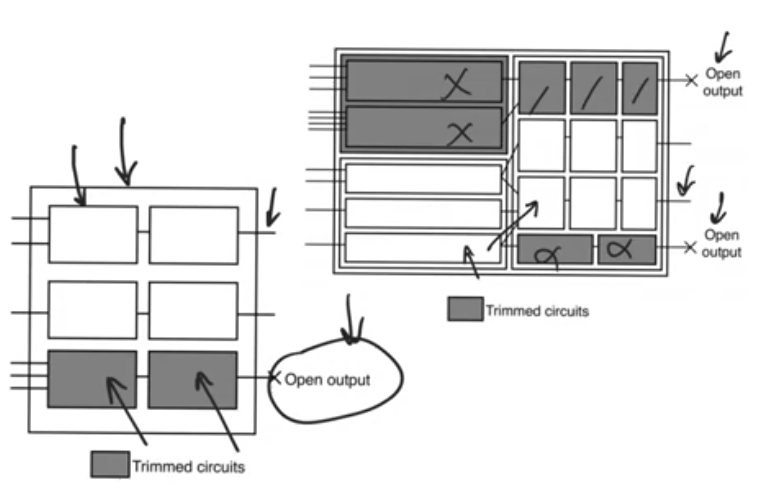
unconnected ports
- When inputs are left open or connected to constant value
- It allows the synthesizer to trim a lot of circuitry
- It trims or remove every logic in the component that is connected to an open circuit or unconnected output
- It’s a good practice to do so cause it allows it to minimize the resource usage
- This is the case with constant inputs, if for example an adder or multiplier have two constant inputs, the synthesizer will remove the hardware, and replace it with a constant value which is the result of the process.
For generate
- for generate syntax to generate a bunch of instances
- It’s not a loop, it’s a way of indicating that we are generating a very large number of the same component
gen_reg: for generation_index int 0 to 15 generate
DFFX : DFF
port map(
D => D(generation_index),
Q => Q(generation_index),
clk => clk);
end generate;
Binding architecture to a component
- Binding a certain architecture to a component while instantiating
- Any instantiation will assume the last entity’s architecture unless otherwise stated
- To choose other architecture, when declaring an instance write the architecture name between () after the entity’s name
Add1: entity word.sixteen_bit_add(behavioral1)
port map(input_a => external_inputa,
input_b => external_inputb,
add_output => internal_inputa);
Add2: entity word.sixteen_bit_add(behavioral2)
port map(input_a => external_inputc,
input_b => external_inputd,
add_output => internal_inputb);